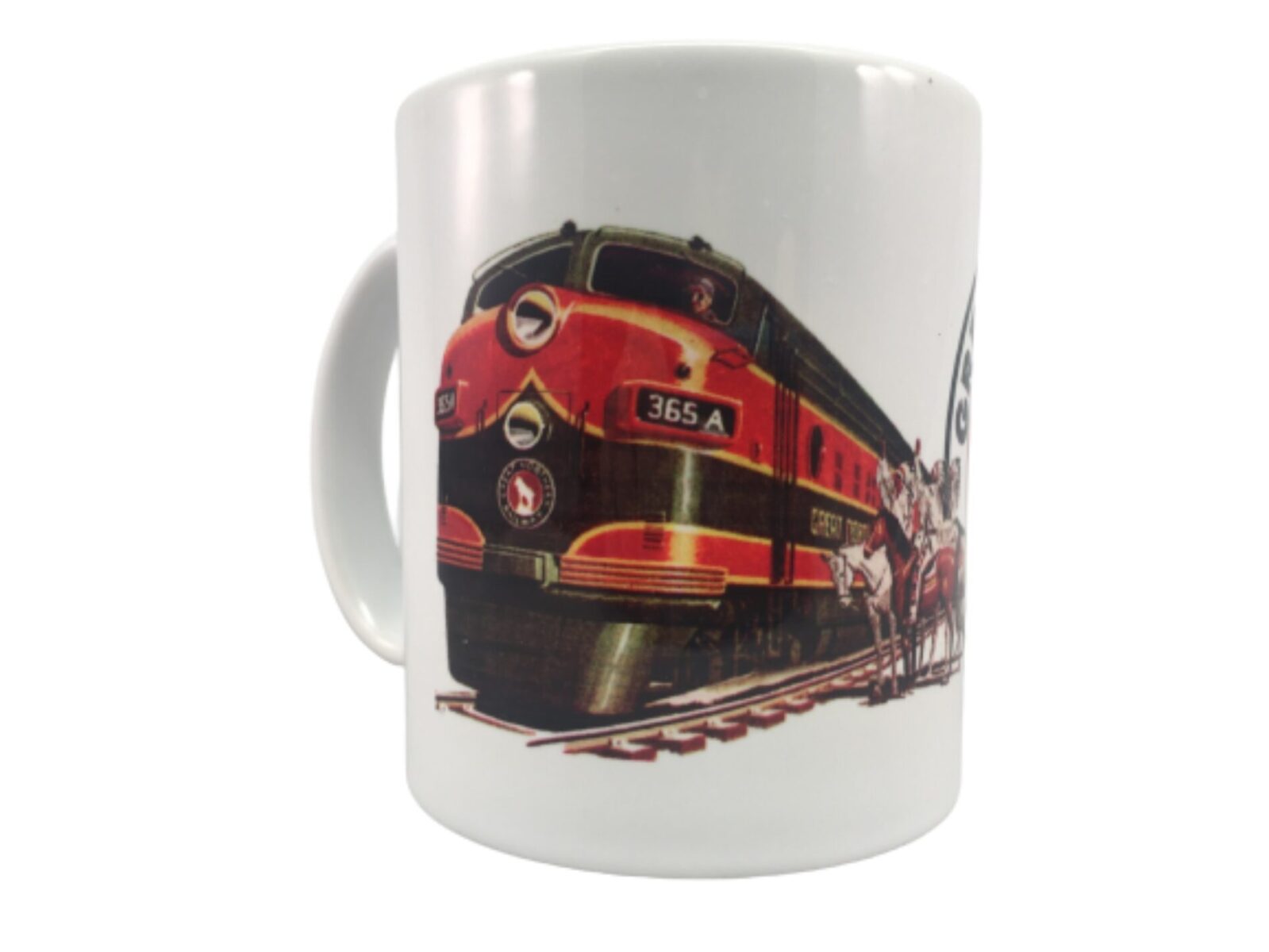
This Great Northern coffee mug features the diesel engine #365A. Printed back and front. Dishwasher and microwave safe. 11 oz.
Learn more from Wikipedia: The Great Northern Railway (reporting mark GN) was an American Class I railroad. Running from Saint Paul, Minnesota, to Seattle, Washington, it was the creation of 19th-century railroad entrepreneur James J. Hill and was developed from the Saint Paul & Pacific Railroad. The Great Northern’s route was the northernmost transcontinental railroad route in the U.S.
In 1970, the Great Northern Railway merged with three other railroads to form the Burlington Northern Railroad, which merged in 1996 with the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway to form the Burlington Northern and Santa Fe Railway.
The Great Northern was built in stages, slowly creating profitable lines, before extending the road further into undeveloped Western territories. In a series of the earliest public relations campaigns, contests were held to promote interest in the railroad and the ranchlands along its route. Fred J. Adams used promotional incentives such as feed and seed donations to farmers getting started along the line. Contests were all-inclusive, from the largest farm animals to the largest freight carload capacity, and were promoted heavily to immigrants and newcomers from the East.[1]
The very first predecessor railroad to the company was the St. Paul and Pacific Railroad owned by William Crooks. He had gone bankrupt running a small line between St. Paul and Minneapolis. He named the locomotive he ran for himself and the William Crooks would be the first locomotive of the Great Northern Railway. J.J. Hill convinced New York banker John S. Kennedy, Norman Kittson (a wealthy fur trader friend), Donald Smith (a Hudson’s Bay Company executive), George Stephen (Smith’s cousin and president of the Bank of Montreal), and others to invest $5.5 million in purchasing the railroad.[2] On March 13, 1878, the road’s creditors formally signed an agreement transferring their bonds and control of the railroad to J.J. Hill’s investment group.[3] On September 18, 1889, Hill changed the name of the Minneapolis and St. Cloud Railway (a railroad which existed primarily on paper, but which held very extensive land grants throughout the Midwest and Pacific Northwest) to the Great Northern Railway. On February 1, 1890, he consolidated his ownership of the StPM&M, Montana Central Railway, and other rail lines to the Great Northern.[4]
The Great Northern had branches that ran north to the Canada–US border in Minnesota, North Dakota, and Montana. It also had branches that ran to Superior, Wisconsin, and Butte, Montana, connecting with the iron range of Minnesota and copper mines of Montana. In 1898 Hill purchased control of large parts of the Messabe Iron Range in Minnesota and its rail lines. The Great Northern began large-scale shipment of ore to the steel mills of the Midwest.[5]
The railroad’s best-known engineer was John Frank Stevens, who served from 1889 to 1903. Stevens was acclaimed for his 1889 exploration of Marias Pass in Montana and determined its practicability for a railroad. Stevens was an efficient administrator with remarkable technical skills and imagination. He discovered Stevens Pass through the Cascade Mountains, set railroad construction standards in the Mesabi Range, and supervised the construction of the Oregon Trunk Line. He then became the chief engineer of the Panama Canal.[6]
The logo of the railroad, a Rocky Mountain goat, was based on a goat William Kenney, one of the railroad’s presidents, had used to haul newspapers as a boy.

















Reviews
There are no reviews yet.